
In addition, NB-IoT focuses specifically on indoor coverage, low cost, long battery life, and high connection density. NB-IoT uses a subset of the LTE standard, but limits the bandwidth to a single narrow-band of 200kHz. It uses OFDM modulation for downlink communication and SC-FDMA for uplink communications. IoT applications which require more frequent communications will be better served by NB-IoT, which has no duty cycle limitations operating on the licensed spectrum.
In March 2019, the Global Mobile Suppliers Association announced that over 100 operators have deployed/launched either NB-IoT or LTE-M networks.This number had risen to 142 deployed/launched networks by September 2019.
In conclusion, NB-Iot characteristics is: wide coverage, low power consumption, low cost, large connection and other characteristics.
1. NB-iot network architecture
- Terminal: Mainly connect to the base station through the air interface. The terminal side mainly includes industry terminals and NB-IoT modules. Industry terminals include: chips, modules, sensor interfaces, terminals, etc.; NB-IoT modules include wireless transmission interfaces, soft SIM devices, sensor interfaces, etc.
- Wireless network side: includes two networking methods, one is Single RAN (Single Radio Access Network, integrated wireless access network), including 2G/3G/4G and NB-IoT wireless networks; the other is NB-IoT is newly built. It is mainly responsible for air interface access processing, cell management and other related functions, and connects to the IoT core network through the S1-lite interface, and forwards non-access layer data to higher-level network elements for processing.
- Core network side: Network elements include two networking modes, one is the integrated Evolved Packet C (Evolved Packet C data transmission mode, welcome to exchange and learn ore, EPC) network elements, including 2G/3G/4G Core network; the other is the core network of the Internet of Things. The core network side supports NB-IoT and eMTC user access through IoT EPC network elements and EPC shared by GSM, UITRAN, and LTE.
- IoT support platform: including HLR (Home Location Register), PCRF (Policy Control and Charging Rules Function), M2M (Machine to Machine, Internet of Things) platform.
- Application server: It is the final gathering point of IoT data, and performs data processing and other operations according to customer needs.

2. NB-IoT application classification
Above all, in the field of low-speed Internet of Things, NB-IoT, as a new standard, achieves the ultimate in cost, coverage, power consumption, and number of connections. This technology is widely used in eight typical industries, including public utilities, healthcare, smart cities, consumers, agricultural environments, logistics and warehousing, smart buildings, and manufacturing.
- Public utilities: meter reading (water/gas/electricity/heat), smart water (pipe network/leakage/quality inspection), smart fire extinguisher/fire hydrant.
- Manufacturing industry: production/equipment status monitoring, energy facilities/oil and gas monitoring, chemical park monitoring, large-scale rental equipment, predictive maintenance (home appliances, machinery, etc.).
- Medical and health: drug traceability, remote medical monitoring, blood pressure meter, blood glucose meter, heart guard monitoring.
- Smart city: smart street lights, smart parking, urban trash can management, public safety/alarm, construction site/urban water level monitoring.
- Logistics warehousing: asset/container tracking, warehouse management, fleet management/tracking, cold chain logistics (status/tracking).

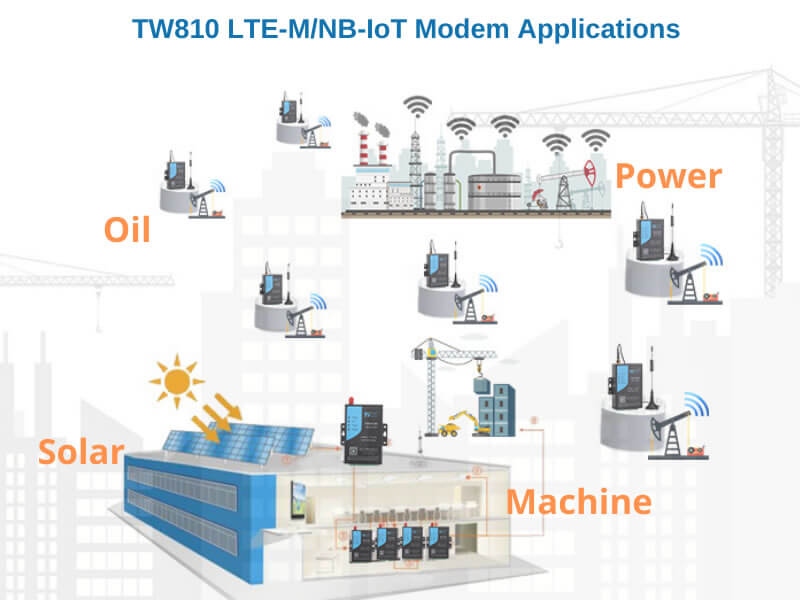
- Smart buildings: access control, smart HVAC, smoke/fire detection, elevator failure/maintenance.
- Consumers: wearable devices, bicycle/moped anti-theft, smart luggage, VIP tracking (children/elderly/pet/vehicle rental), payment/POS machines.
- Agricultural environment: precision planting (environmental parameters: water/temperature/light/medicine/fertilizer), animal husbandry (health/tracking), aquaculture, food safety traceability, urban environmental monitoring (water pollution/noise/air quality PM2.5) .



Comment