-
Communication mode of VXLAN
-
(1) Routing mode: Communication between different network segments
End to End communication:
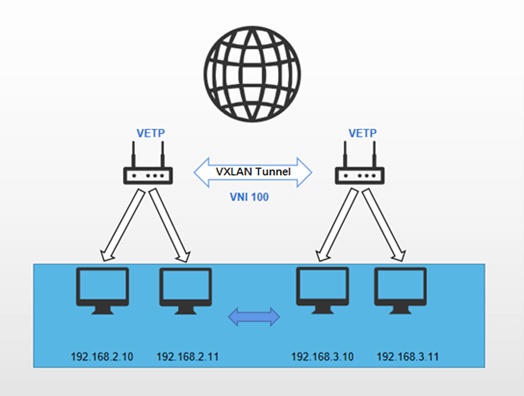
The two end devices establish a direct VXLAN tunnel, through which all data traffic is transmitted. The subnets on both devices form a unified Layer 2 subnet.
Multiterminal forward communication:
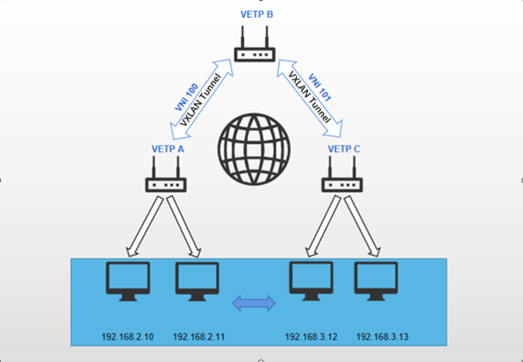
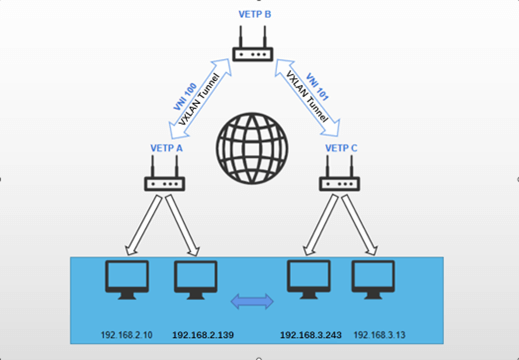
The objective is to establish a VXLAN tunnel between Device A and Device B, while simultaneously enabling Device C to also establish a VXLAN tunnel with Device B. This configuration facilitates the formation of a unified layer 2 subnet for the devices within subnets under both Device A and Device C, requiring potential data forwarding through multiple tunnels to reach its intended destination.
-
(2) Bridge mode: Communicates with a Network Segment
End to End communication:
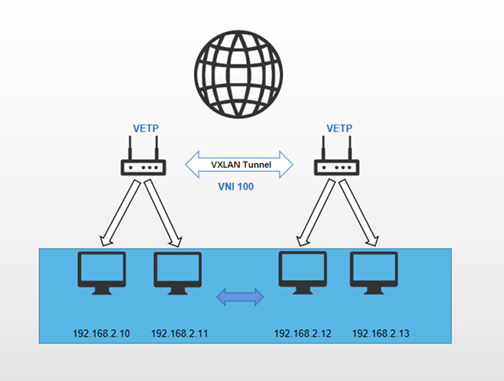
The two end devices establish a direct VXLAN tunnel, through which all data traffic is transmitted. The subnets on both devices form a unified Layer 2 subnet.
Multiterminal forward communication:
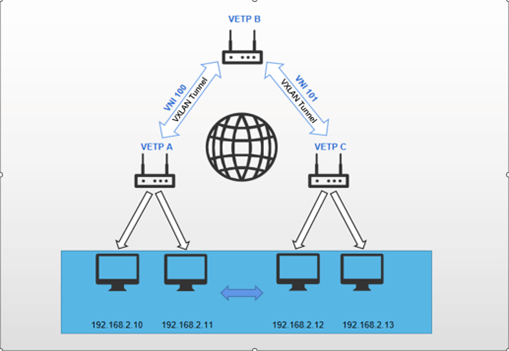
Establish a VXLAN tunnel between Device A and Device B, while also configuring a VXLAN tunnel between Device C and Device B. This configuration enables the subnet devices under both Device A and Device C to form a unified layer 2 subnet, with data potentially being forwarded through multiple tunnels in order to reach its intended destination.
-
Settings of VXLAN
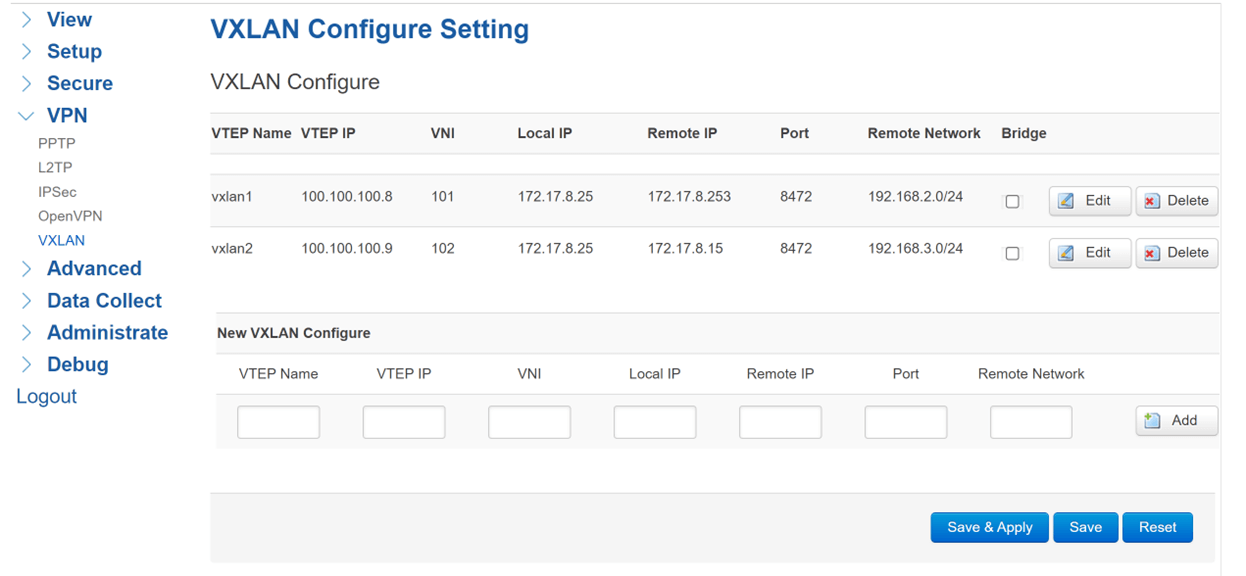
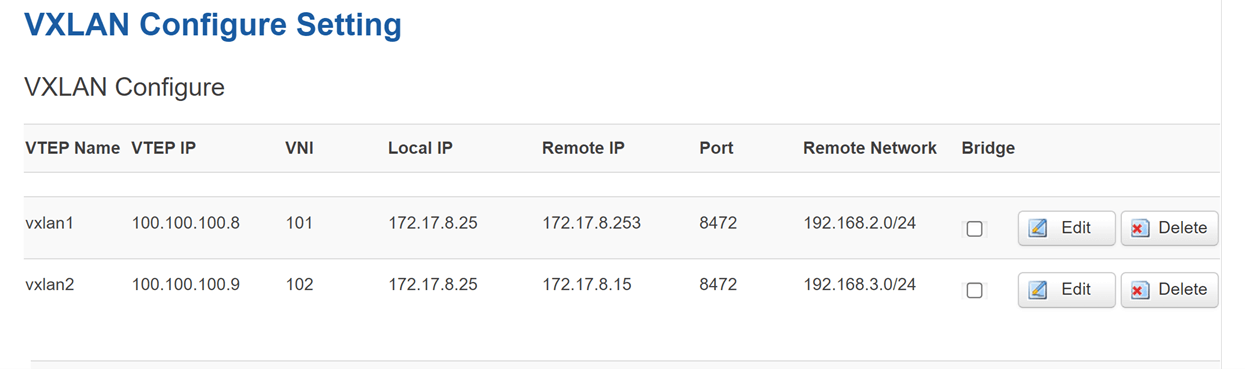
- VTEP Name: VTEP name and virtual NIC device name; Example: vxlan0-n
- VTEP IP: Virtual network adapter device IPaddr;
- VNI: The unique identifier of the tunnel must be the same as the VNI of the peer device. The VNI rules must be unique;
- Local IP: The WAN IP address of the local VTEP;
- Remote IP: WAN IP address of the peer VTEP;
- Port: UDP port number used by the VXLAN. The default UDP port number is 8472;
- Remote Network: Specifies the subnet of the peer VTEP;
- Bridge: The default mode is route mode. Select Bridge mode to enable.
-
Example of VXLAN
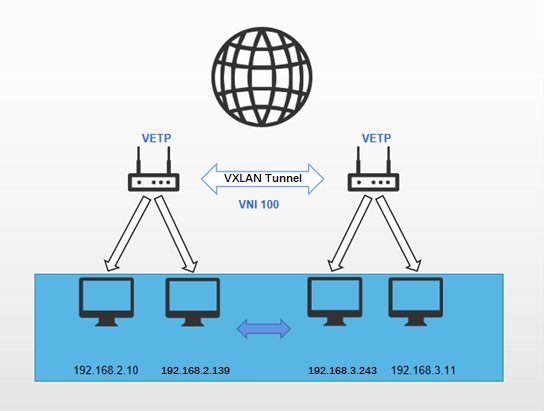
End to End communication:
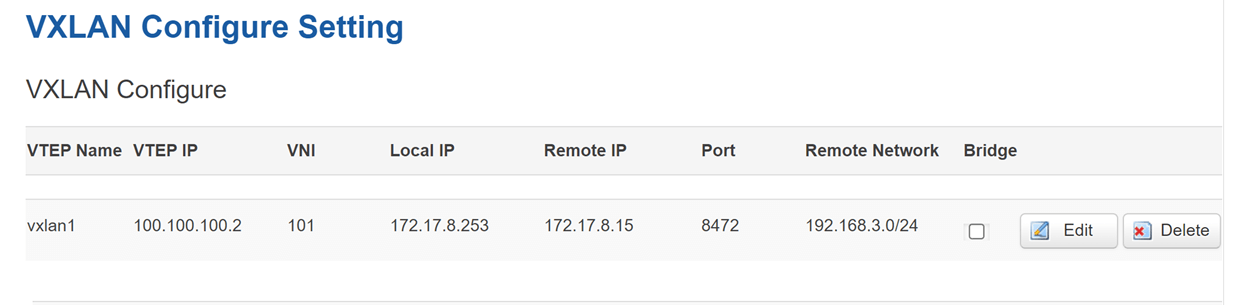
Device A settings:
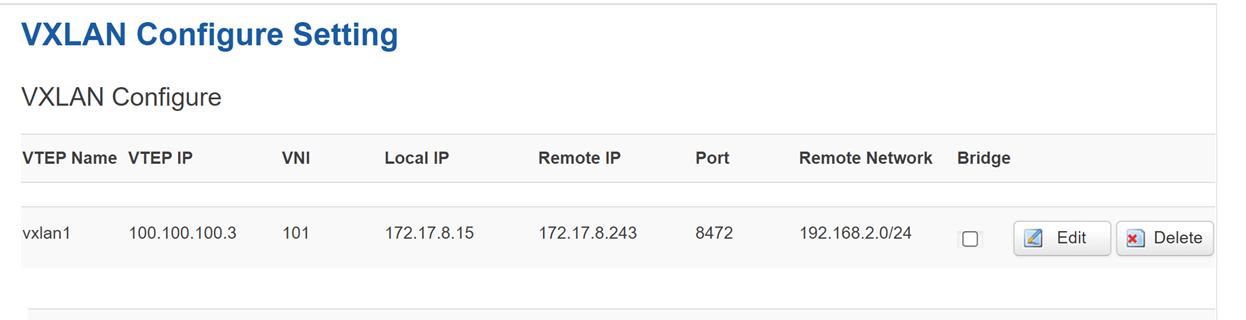
Device B settings:
Test Result:
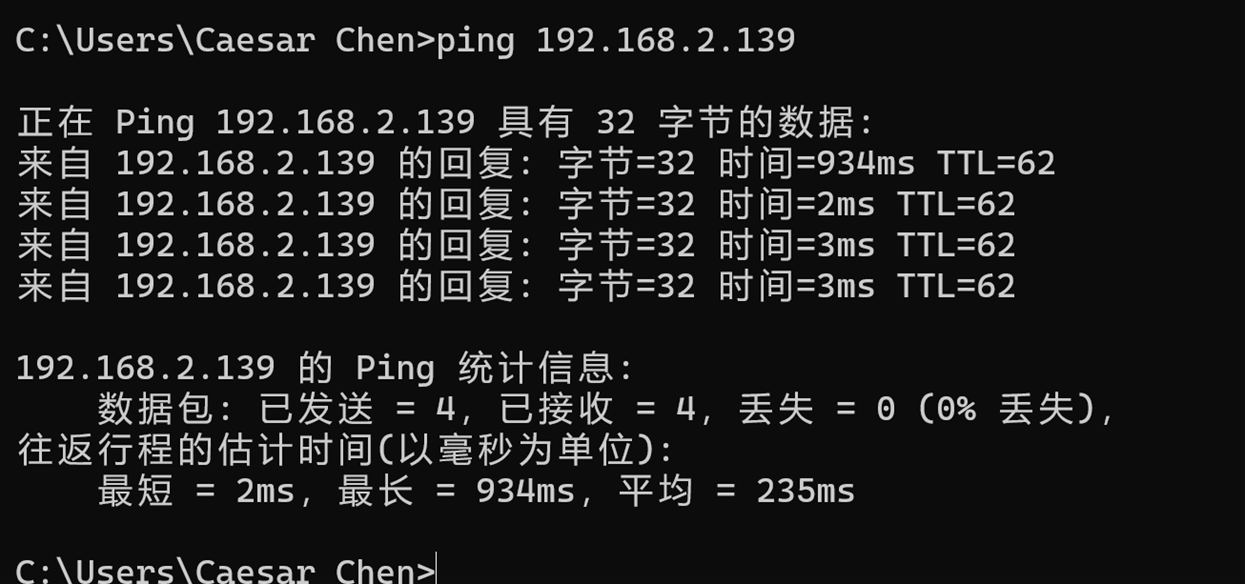
Ping subdevice of device A (192.168.2.139) from subdevice of device B (192.168.3.243)
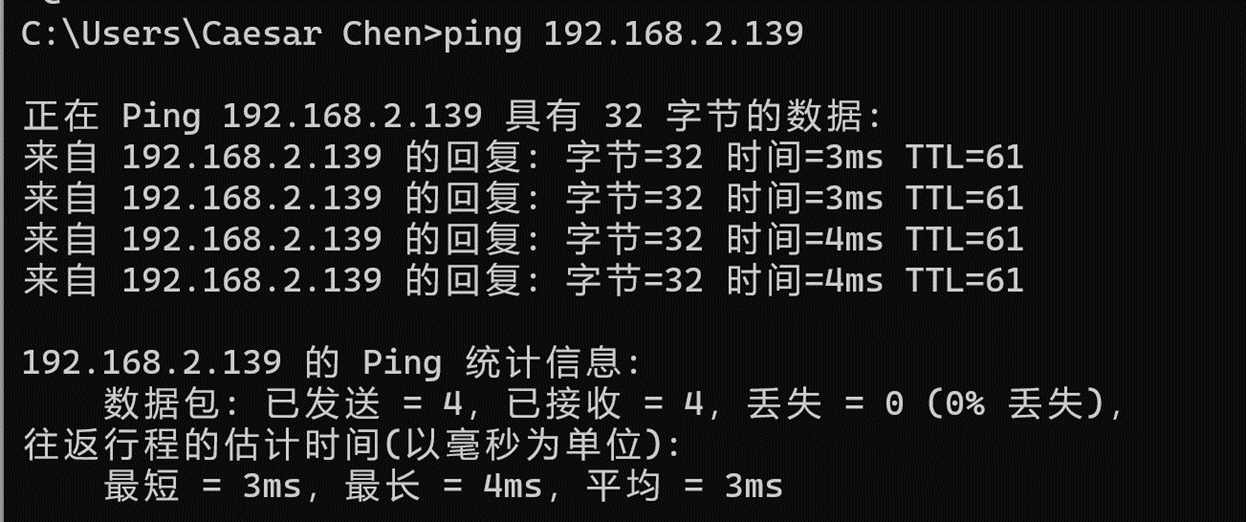
Ping the subdevice of device B (192.168.3.243) from the subdevice of device A (192.168.2.139)
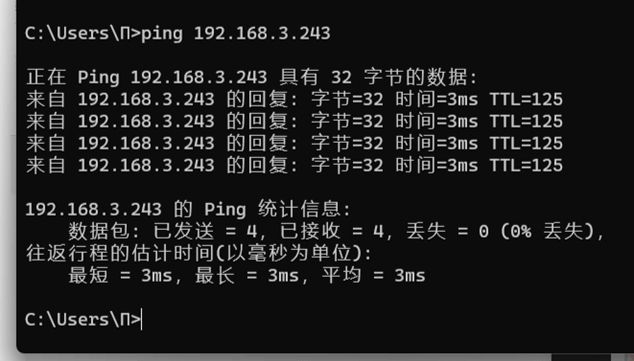
Multiterminal forward communication:
Device B settings:
Device A settings:
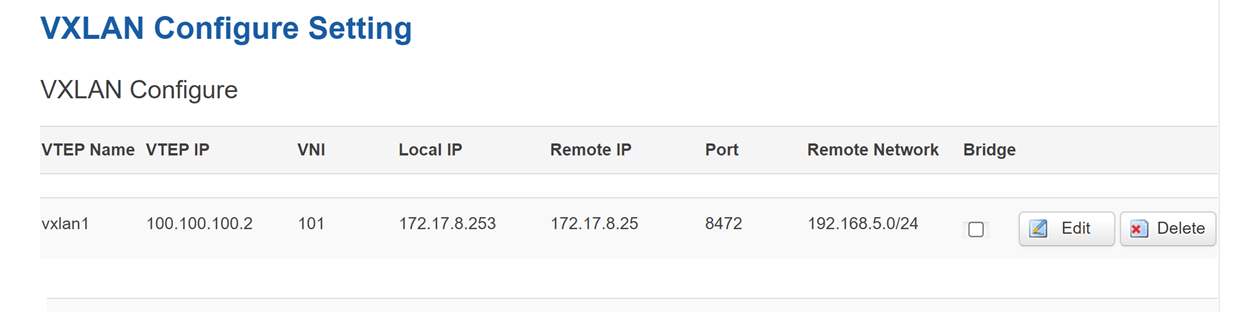
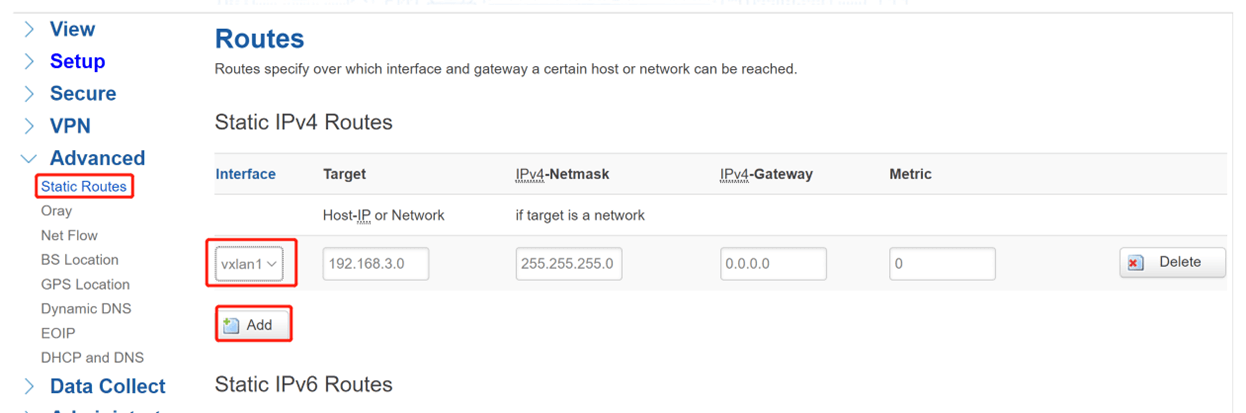
For Device A, also need to add new Static Routes of vxlan1(VTEP Name), add the Host IP of Device C. Here we set 192.168.3.0/255.255.255.0/0.0.0.0/0.
Device C settings:
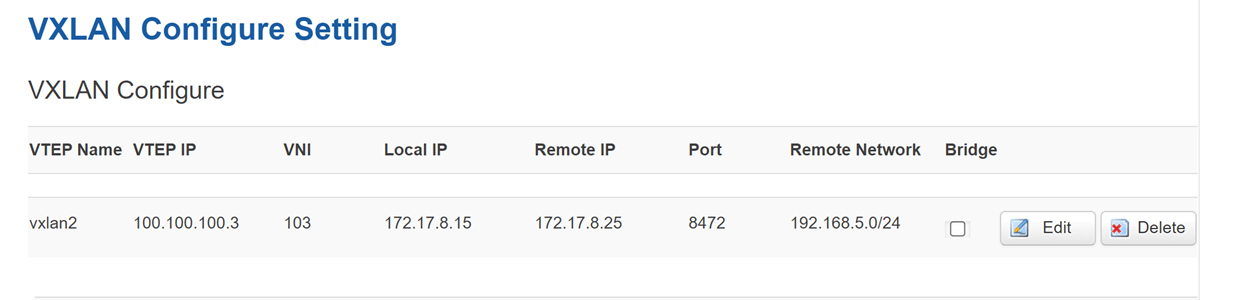
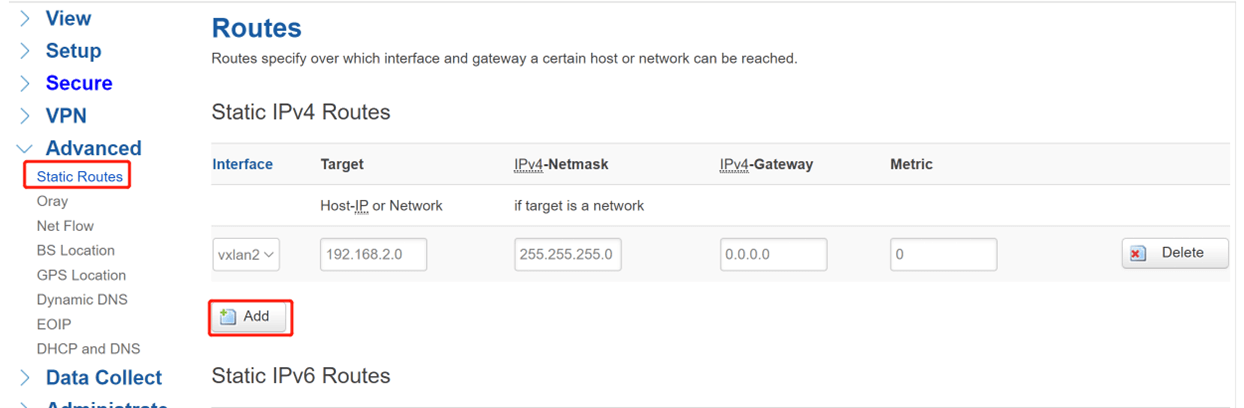
For Device C, also need to add new Static Routes of vxlan2(VTEP Name), add the Host IP of Device A. Here we set 192.168.2.0/255.255.255.0/0.0.0.0/0.
Test Result:
Ping the subdevice of device C (192.168.3.243) from the subdevice of device A (192.168.2.139)
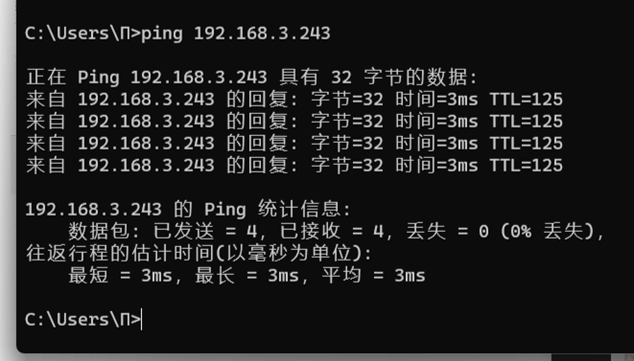
Ping the subdevice of device A (192.168.2.139) from subdevice of device C (192.168.3.243)
Relevant Resources:



Comment