How to Monitor Ammonia Gas in a Plant Using a 5G IoT Gateway
Ammonia is widely used in industries, especially in fertilizers, but it can be hazardous due to its toxicity and potential for explosion. Monitoring ammonia gas levels is essential for ensuring safety and compliance in ammonia plants. With advancements in technology, utilizing a 5G IoT gateway for real-time monitoring has become increasingly feasible and efficient. This article outlines how to set up an effective monitoring system using a 5G IoT gateway, including alarms, fault detection, and warning systems.

Image from Canva
Overview of the System Components
1. 5G IoT Gateway
The 5G IoT gateway serves as the central hub for data collection and communication. With low latency and high-speed connectivity, it is perfectly suited for real-time monitoring applications.

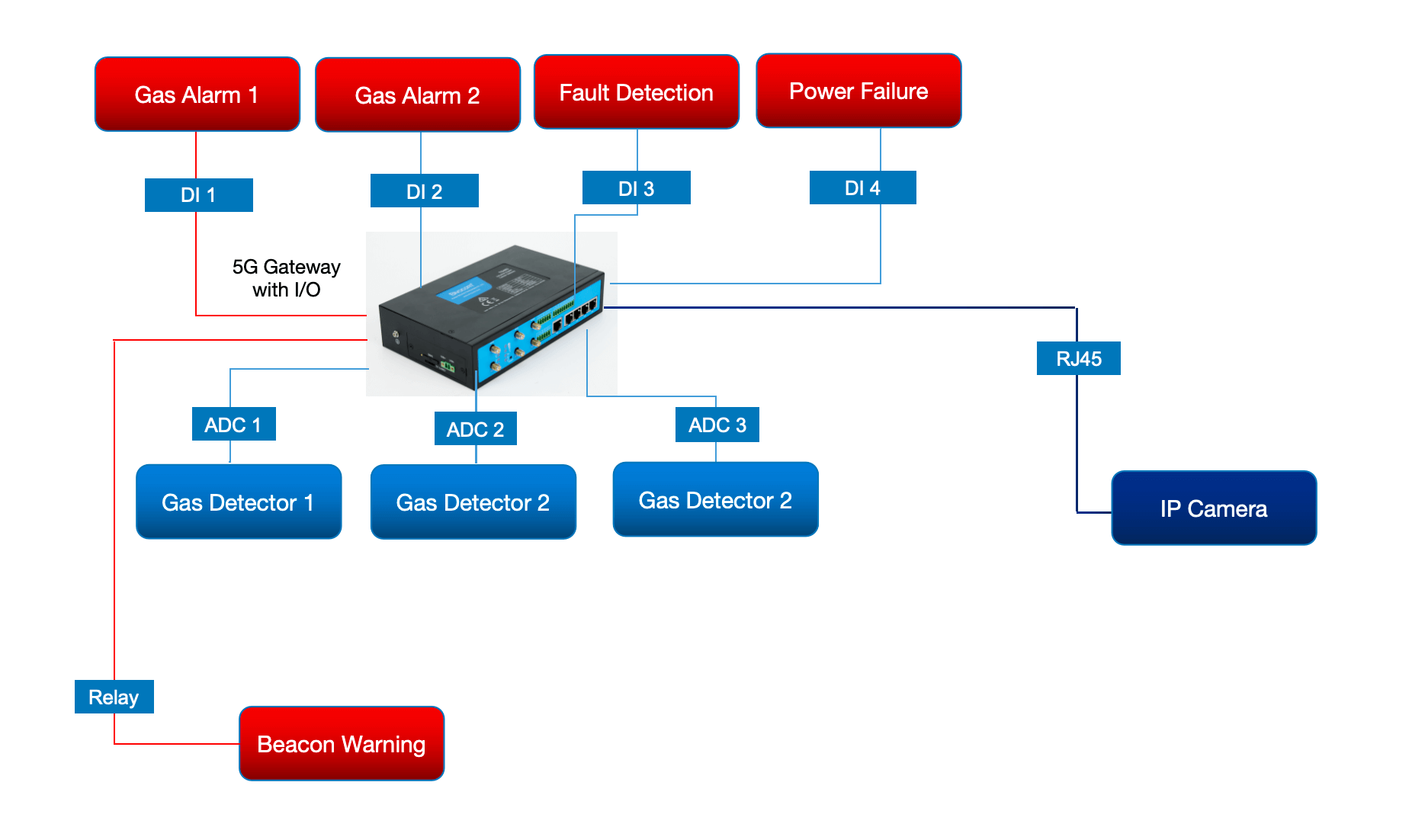
2. Digital Inputs and Outputs
- 4 Digital Inputs (DI):
- 2 for Alarm: Dedicated digital inputs for high-level ammonia gas alarms.
- 1 for Fault Detection: Detects any faults in the monitoring system itself.
- 1 for General Power Failure: Monitors the power supply status to ensure continuous operation.
3. Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC)
- 3 ADCs: These convert analog signals from gas detectors into digital data, allowing for precise readings of ammonia gas concentrations.
4. Gas Detector
Gas detectors are essential for detecting the levels of ammonia. They provide the necessary inputs to the ADCs, enabling the system to continuously monitor gas levels.
5. Relay and Beacon Warning System
- 1 Relay: This is used to activate warning systems or shut down systems in case of a high ammonia concentration.
- Beacon Warning: A visual alarm that activates in case of an ammonia leak, alerting personnel in the vicinity.
6. Ethernet Ports
- 2 Ethernet Ports: These allow for the connection of the IoT gateway to local networks and remote monitoring systems, facilitating data transmission and system management.
7. Software Components
- Node-Red: A visual programming tool that helps in wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services to create a monitoring dashboard.
- Python Programmable: Python can be used to write scripts for custom monitoring logic, handling data processing, and ensuring system integration.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up the Monitoring System
Step 1: Hardware Installation
- Install the 5G IoT Gatewayclose to the areas where ammonia gas detection will occur.
- Connect the gas detectorsto the ADCs. Ensure that the detectors are calibrated and configured for the specific ammonia concentrations of concern.
- Wire the alarms, fault detection, and power failure inputs to the digital inputs of the IoT gateway.
Step 2: Configure the Software
- Set Up Node-Redon the gateway. Use its drag-and-drop interface to create flows that will read data from the ADCs and DI inputs.
- Develop Python Scriptsto process the data received from the ADCs. Include logic to evaluate gas levels and send notifications for alarms, faults, or power failures.
Step 3: Establish Communication
- Utilize the Ethernet Portsto connect the IoT gateway to a local network. This enables data transmission to cloud services or local monitoring systems.
- Set up secure communications and ensure that data can be accessed by authorized personnel only.
Step 4: Implement the Warning System
- Integrate the Relay and Beacon Warning Configure the relay to trigger the beacon when specific alarm conditions are met.
- Test the warning systems to ensure they operate correctly during simulated faults or gas leak scenarios.
Step 5: Testing and Calibration
- Run teststo ensure that the system reacts accurately to actual gas levels.
- Calibrate the gas detectorsas needed to fine-tune the readings and alarm thresholds.
Step 6: Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
- Use Node-Red to create a dashboard for real-time monitoring, displaying gas concentrations and system status.
- Schedule periodic maintenance checks and recalibrations for gas detectors and alarms.
Conclusion
Implementing a 5G IoT gateway for ammonia gas monitoring not only enhances safety but also improves operational efficiency. The combination of digital and analog inputs, alongside real-time alert systems, ensures that any ammonia leak is detected promptly. By leveraging tools like Node-Red for visualization and Python for custom logic, industries can establish a robust monitoring system that safeguards personnel and minimizes risk.
By adhering to these steps, ammonia plants can create a reliable monitoring solution that meets industry standards and protects both people and the environment. Stay safe, and keep monitoring!



Comment