Have you ever wonder what is port forward on IoT router, and why we need port forward, what is used for? Let’s bring these question to read this article, which will tell you more about port forward, and how to enable port forward on IoT router, as well as 2 examples of configure port forward on an IoT router.
- What is Port Forward?
Port forward is also called port mapping, virtual server, and NAT. Different brands of IoT routers have different names, but the operation is similar.
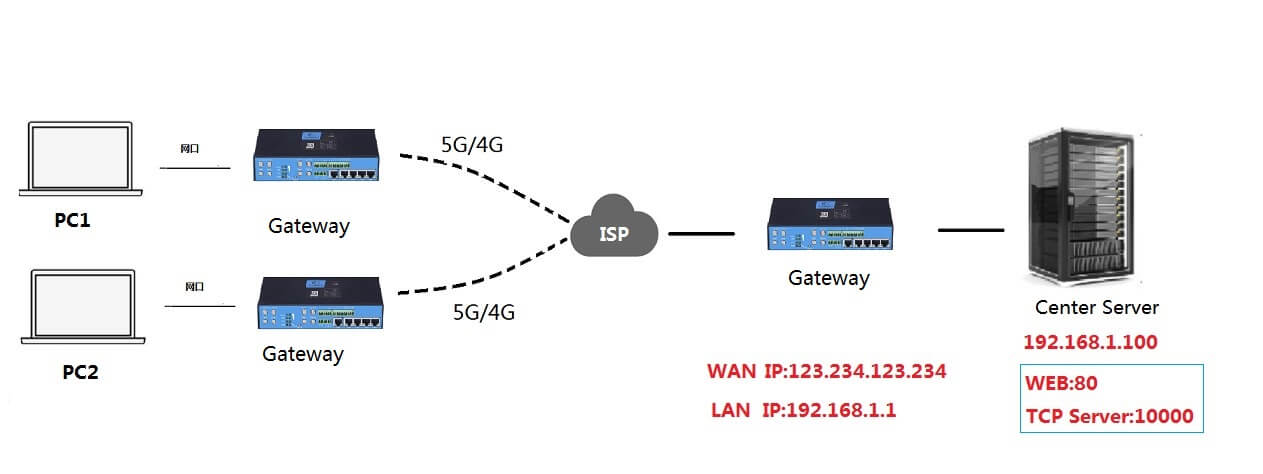
For example, there is a server (IP: 192.168.1.100) in the intranet connected to a router with a fixed public network IP to access the Internet, and there are two computers in different places in the external network to access the web platform of the server (let’s say port 80) and other application programs (let’s say port 10000), the topology diagram is as below:
When we configure port forwarding rules, please note the following details:
- The external port does not have to be the same as the internal port, the PC only needs to access the external network IP and external port of the mapped device, and the router can forward the data to the internal port corresponding to the internal network server.
- When the external network is a fixed public network IP, try to avoid using ports 80 and 443 for external ports, because these ports need to be filed before they can be accessed directly.
- Port forward generally requires a relatively fixed public network IP on the side to be mapped, so it is generally suitable for wired networks, local area networks, VPN networks, and private SIM cards with fixed public network IP. If the SIM card doesn’t have a public network IP and cannot penetrate the operator network, there is no direct port mapping.
- Intranet IP device shall config router’s LAN IP as it’s gateway IP address, and the firewall should open its server port.
- How to Enable Port Forward?
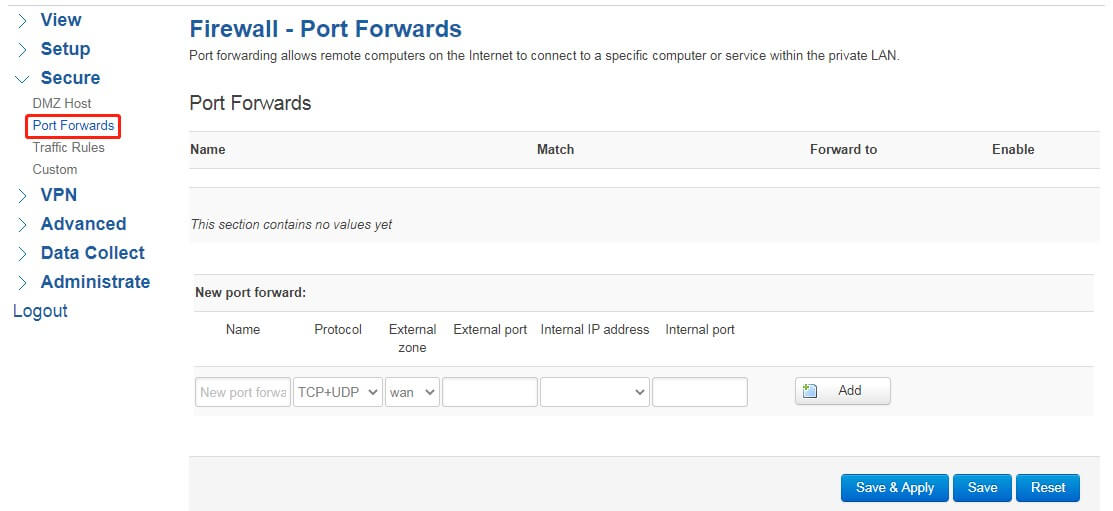
Name: You can name it, or leave it blank, which will be automatically generated.
Protocol: mapping type, which can be TCP, UDP, or both TCP/UDP.
External area: generally based on wan port mapping, if it needs to be based on backup wan, select swan, while if it is based on VPN interface, select VPN.
External port: The external port is the port provided for external network access, and does not have to be the same as the port provided internally. External port can be a ranged from “10000-12000”
Intranet IP: the host IP that provides the service.
Internal Port: The internal port on which the service is provided. internal port can be a ranged from “10000-12000”
- Examples
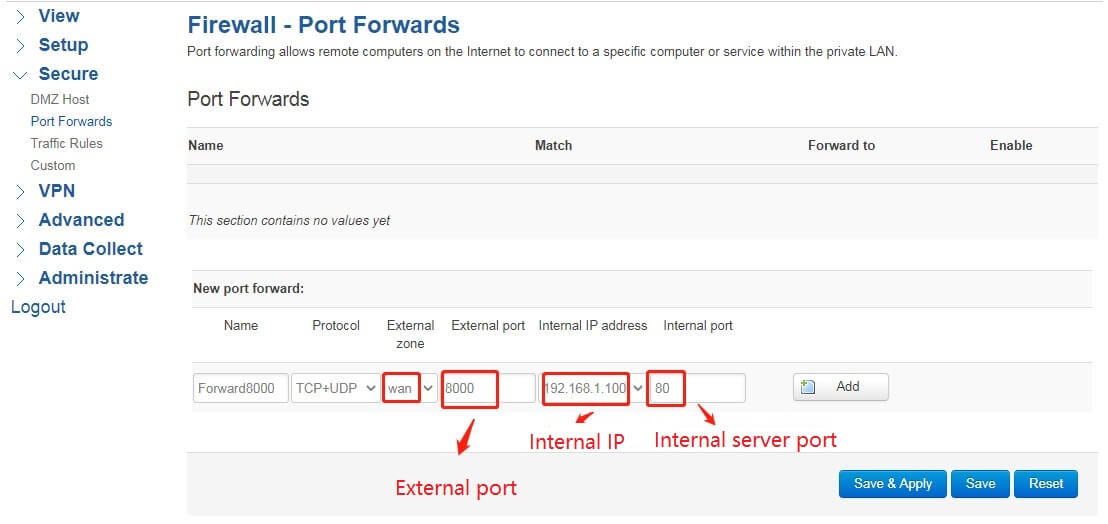
Example 1: Map port 80 of 192.168.1.100 to port 8000 of the public network, the configuration is as follows:
Example 2: Map port 10000 of 192.168.1.100 to port 10000 of the public network, the configuration is as follows:
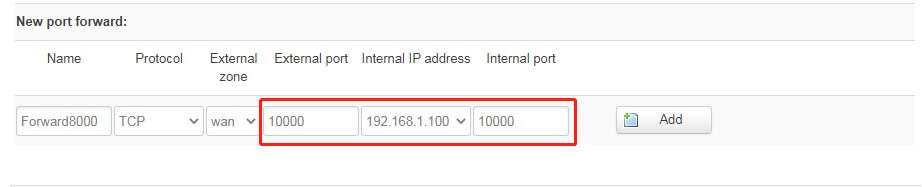
Image source: panumas nikhomkhai



Comment