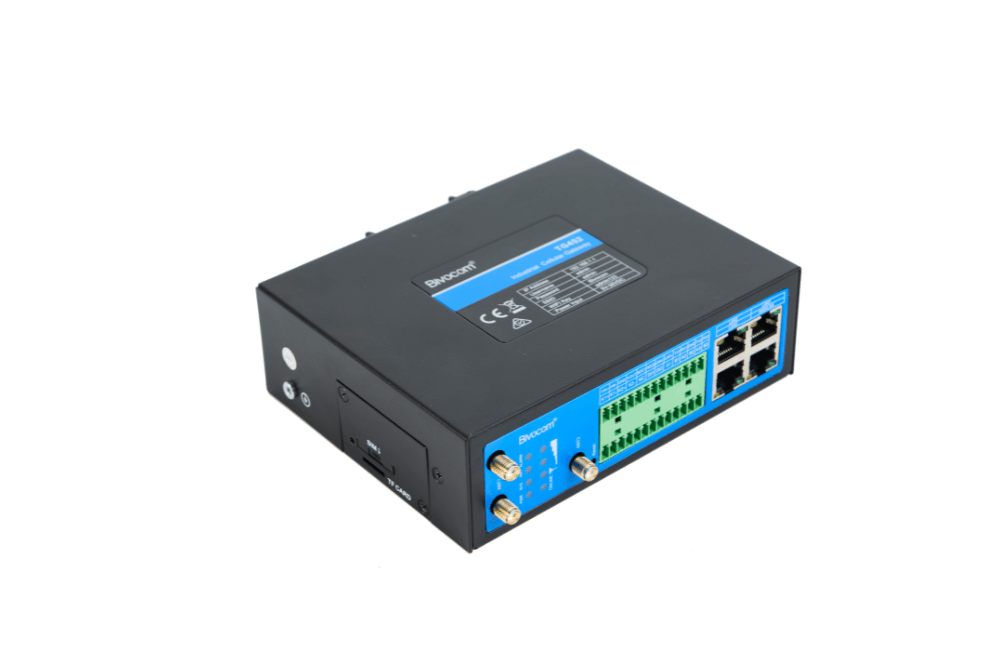
What is LoRa and LoRaWAN?
LoRa Gateways
Bivocom's LoRa solutions perfectly complement 4G networks by providing a low-power, long-range alternative for IoT applications. While 4G excels at high-speed data transfer, LoRa efficiently covers vast areas with minimal power consumption, making it ideal for numerous IoT deployments.
LoRa and LoRaWAN are related but distinct concepts in low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN). Here’s a breakdown!
1. LoRa (Long Range)
1)Definition: LoRa refers to the physical layer technology that uses a unique modulation scheme (based on Chirp Spread Spectrum) to enable long-range wireless communication.
2)Key Features:
Long Range: Can transmit data over several kilometers.
Low Power: Designed for low power consumption, making it ideal for battery-operated devices.
2. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
1) Definition: LoRaWAN is a network protocol that operates on top of LoRa technology. It defines how devices communicate over a LoRa network.
2) Key Features:
Network Architecture: It includes specifications for network components like gateways, network servers, and application servers.
Communication Protocol: LoRaWAN manages communication between devices to ensure data is sent efficiently and securely.
Device Management: It includes features for device authentication and security.
3. Key Differences
1) Layer:
LoRa: Physical layer (modulation technology).
LoRaWAN: Network layer (protocol for communication).
2) Functionality:
LoRa: Focused on long-range, low-power transmission.
LoRaWAN: Governs how devices connect to the network and manage communication.
3) Scope:
LoRa: Just one part of the system for wireless communication.
LoRaWAN: Encompasses the entire network experience, including gateways and services.
In short, LoRa provides the technology to communicate over long distances, while LoRaWAN creates the rules and framework to enable devices to work together seamlessly.
1. LoRa (Long Range)
1)Definition: LoRa refers to the physical layer technology that uses a unique modulation scheme (based on Chirp Spread Spectrum) to enable long-range wireless communication.
2)Key Features:
Long Range: Can transmit data over several kilometers.
Low Power: Designed for low power consumption, making it ideal for battery-operated devices.
2. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
1) Definition: LoRaWAN is a network protocol that operates on top of LoRa technology. It defines how devices communicate over a LoRa network.
2) Key Features:
Network Architecture: It includes specifications for network components like gateways, network servers, and application servers.
Communication Protocol: LoRaWAN manages communication between devices to ensure data is sent efficiently and securely.
Device Management: It includes features for device authentication and security.
3. Key Differences
1) Layer:
LoRa: Physical layer (modulation technology).
LoRaWAN: Network layer (protocol for communication).
2) Functionality:
LoRa: Focused on long-range, low-power transmission.
LoRaWAN: Governs how devices connect to the network and manage communication.
3) Scope:
LoRa: Just one part of the system for wireless communication.
LoRaWAN: Encompasses the entire network experience, including gateways and services.
In short, LoRa provides the technology to communicate over long distances, while LoRaWAN creates the rules and framework to enable devices to work together seamlessly.
LoRa and LoRaWAN History
1. LoRa (Long Range)
1) Origin: Developed by Semtech in the early 2000s. The technology was initially aimed at providing long-range communication for various applications.
2) Key Development: In 2013, LoRa was developed as a modulation technique allowing long-distance communication with low power requirements.
2. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
1) Standardization: In 2015, the LoRa Alliance was formed to promote the development and adoption of LoRaWAN as a standard for LPWAN. This was crucial for ensuring interoperability between devices and networks.
2) Specifications: The first version of the LoRaWAN protocol was released in 2015, outlining how devices communicate over a LoRa network.
3) Growth: Since then, LoRaWAN has gained widespread adoption in various IoT applications, enabling smart cities, agriculture, and supply chain monitoring.
2. Recent Developments
1) Expansion: Over the years, LoRa and LoRaWAN have continued to evolve, with more features and enhanced capabilities to improve connectivity and security. Global
2) Adoption: By the late 2010s and into the 2020s, LoRaWAN networks became widespread, with many cities implementing it for smart applications. The technology has transformed IoT connectivity, making it easier for devices to communicate over long distances while conserving energy
1) Origin: Developed by Semtech in the early 2000s. The technology was initially aimed at providing long-range communication for various applications.
2) Key Development: In 2013, LoRa was developed as a modulation technique allowing long-distance communication with low power requirements.
2. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
1) Standardization: In 2015, the LoRa Alliance was formed to promote the development and adoption of LoRaWAN as a standard for LPWAN. This was crucial for ensuring interoperability between devices and networks.
2) Specifications: The first version of the LoRaWAN protocol was released in 2015, outlining how devices communicate over a LoRa network.
3) Growth: Since then, LoRaWAN has gained widespread adoption in various IoT applications, enabling smart cities, agriculture, and supply chain monitoring.
2. Recent Developments
1) Expansion: Over the years, LoRa and LoRaWAN have continued to evolve, with more features and enhanced capabilities to improve connectivity and security. Global
2) Adoption: By the late 2010s and into the 2020s, LoRaWAN networks became widespread, with many cities implementing it for smart applications. The technology has transformed IoT connectivity, making it easier for devices to communicate over long distances while conserving energy
LoRa for IoT Applications
Due to its long-range and low-power capabilities, LoRa technology is widely used in various Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Here are some common applications!
1. Smart Agriculture
Usage: Soil moisture monitoring, livestock tracking, and crop health monitoring.
Benefits: Reduces water usage and enhances crop yield.
2. Smart Cities
Usage: Smart street lighting, waste management (smart bins), and air quality monitoring.
Benefits: Improves urban management and resource efficiency.
3. Industrial IoT
Usage: Equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, and asset tracking.
Benefits: Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Usage: Wildlife tracking, weather stations, and disaster management (flood, fire).
Benefits: Provides real-time data for better conservation and response.
5. Smart Metering
Usage: Water, gas, and electricity metering.
Benefits: Enables remote monitoring and reduces operational costs.
6. Healthcare
Usage: Remote patient monitoring and tracking of medical equipment.
Benefits: Improves patient care and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
7. Supply Chain and Logistics
Usage: Asset tracking and temperature monitoring for goods in transit.
Benefits: Ensures product quality and improves logistics efficiency.
8. Home Automation
Usage: Smart thermostats, security systems, and energy management systems.
Benefits: Increases convenience and energy efficiency in homes.
LoRa's versatility makes it suitable for many applications where long-range communication and low power consumption are essential!
1. Smart Agriculture
Usage: Soil moisture monitoring, livestock tracking, and crop health monitoring.
Benefits: Reduces water usage and enhances crop yield.
2. Smart Cities
Usage: Smart street lighting, waste management (smart bins), and air quality monitoring.
Benefits: Improves urban management and resource efficiency.
3. Industrial IoT
Usage: Equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, and asset tracking.
Benefits: Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Usage: Wildlife tracking, weather stations, and disaster management (flood, fire).
Benefits: Provides real-time data for better conservation and response.
5. Smart Metering
Usage: Water, gas, and electricity metering.
Benefits: Enables remote monitoring and reduces operational costs.
6. Healthcare
Usage: Remote patient monitoring and tracking of medical equipment.
Benefits: Improves patient care and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
7. Supply Chain and Logistics
Usage: Asset tracking and temperature monitoring for goods in transit.
Benefits: Ensures product quality and improves logistics efficiency.
8. Home Automation
Usage: Smart thermostats, security systems, and energy management systems.
Benefits: Increases convenience and energy efficiency in homes.
LoRa's versatility makes it suitable for many applications where long-range communication and low power consumption are essential!